Nutritional Profile of Green Apples
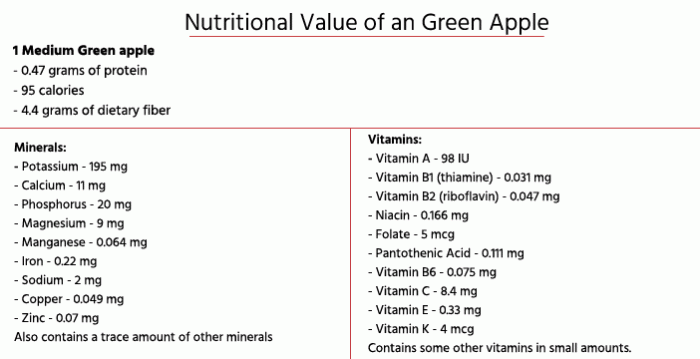
Green apple nutrition facts – Green apples, a crisp and refreshing fruit, offer a surprising array of nutrients beneficial to overall health. They are a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to a balanced diet. This section details the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of a medium-sized green apple (approximately 182 grams), providing a clearer understanding of their nutritional value.
Macronutrient Composition of Green Apples
The following table summarizes the macronutrient content of a medium-sized green apple:
| Nutrient | Amount per serving | % Daily Value | Unit of Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 25g | 8% | grams |
| Protein | 0.5g | 1% | grams |
| Fat | 0.3g | 0% | grams |
Note that the percentage daily values are approximate and can vary depending on individual dietary needs and recommended daily intake.
Micronutrient Content of Green Apples
Green apples are a valuable source of several essential vitamins and minerals. These micronutrients play crucial roles in various bodily functions, contributing to overall well-being.
Green apples contain a range of vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system and collagen production.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health.
- Potassium: An important electrolyte that helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
- Manganese: A mineral involved in bone formation, wound healing, and metabolism.
Fiber Content and its Role in Digestion
A medium-sized green apple provides approximately 4 grams of dietary fiber. Fiber is indigestible plant matter that plays a vital role in digestive health. It adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Furthermore, fiber contributes to a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management. The fiber in green apples also supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, contributing to a healthy gut microbiome.
A healthy gut microbiome is increasingly recognized for its impact on overall health, influencing everything from immunity to mental well-being.
Health Benefits Associated with Green Apple Consumption
Green apples, a crisp and refreshing fruit, offer a surprising array of health benefits beyond their delightful taste. Their nutritional profile contributes to various aspects of well-being, from aiding weight management to supporting cardiovascular health. This section delves into the specific ways in which incorporating green apples into your diet can positively impact your overall health.
Weight Management and Green Apples
Green apples are a valuable asset in weight management strategies due to their high fiber and water content. The fiber in green apples promotes satiety, meaning you feel fuller for longer after consuming them, reducing overall calorie intake. The high water content further contributes to this feeling of fullness, helping to curb appetite and prevent overeating. A single medium-sized green apple contains roughly 4 grams of fiber and significant amounts of water, making it a naturally filling and low-calorie snack.
For example, replacing a high-calorie snack with a green apple can contribute to a daily calorie deficit, crucial for sustainable weight loss.
Antioxidant Properties and Overall Health
Green apples are a good source of antioxidants, primarily polyphenols like quercetin and catechin. These compounds combat oxidative stress, a process linked to various chronic diseases including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of these conditions. The vibrant green color of the apple itself is an indicator of its high concentration of these beneficial compounds.
Regular consumption of green apples, as part of a balanced diet, can contribute to a stronger antioxidant defense system within the body.
Green apples are a low-calorie, nutrient-rich snack, offering fiber and vitamin C. However, comparing their nutritional profile to something like a fast-food option reveals a stark contrast; for instance, checking out the quarter pounder nutrition facts highlights the significant difference in fat and calorie content. Returning to the green apple, its nutritional benefits are clear when considering a balanced diet.
Green Apples and Cardiovascular Health
The fiber, antioxidants, and other components in green apples contribute to improved cardiovascular health. The soluble fiber helps lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, while the antioxidants protect against damage to blood vessels. Furthermore, green apples contain potassium, an essential mineral that helps regulate blood pressure. Studies have shown a correlation between regular fruit consumption, including apples, and a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
This effect is likely due to the synergistic action of the various beneficial compounds found within the fruit.
Nutritional Comparison of Green Apples to Other Fruits, Green apple nutrition facts
While many fruits offer health benefits, green apples stand out in certain aspects. Compared to fruits high in sugar, such as bananas or mangoes, green apples offer a lower glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This makes them a suitable choice for individuals managing diabetes. Compared to citrus fruits, green apples provide a different profile of antioxidants and vitamins.
While oranges are rich in Vitamin C, green apples offer a broader spectrum of polyphenols. Ultimately, a varied diet including a range of fruits is optimal for overall health, but green apples offer a unique combination of nutrients that support specific health goals.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations: Green Apple Nutrition Facts

While green apples offer numerous health benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential drawbacks associated with their consumption, particularly in excessive quantities. Understanding these aspects allows for informed and responsible enjoyment of this nutritious fruit.
Overconsumption of any fruit, including green apples, can lead to several issues. The high fiber content, while beneficial in moderation, can cause digestive discomfort such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea if consumed in large amounts. Furthermore, the natural sugars present can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with a healthy overall diet and sufficient physical activity.
Individual sensitivities and allergic reactions, although rare, are also a possibility. Some individuals might experience skin rashes, itching, or other allergic symptoms after consuming green apples.
Glycemic Index and Metabolic Considerations
Green apples possess a moderate glycemic index (GI), generally ranging from 30 to 40, depending on factors like ripeness and variety. This means they cause a relatively slow and gradual rise in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. However, individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance should still monitor their green apple intake as part of their overall carbohydrate management plan.
Consuming a large quantity of green apples, even with a moderate GI, could still lead to a noticeable blood sugar spike. For example, eating three or four large green apples in a single sitting could potentially negatively impact blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to determine the appropriate portion size for individual needs.
Pesticide Residue and Minimizing Exposure
Commercially grown green apples, like many other fruits and vegetables, may contain pesticide residues. While generally within acceptable safety limits set by regulatory agencies, minimizing exposure is advisable. Washing green apples thoroughly under running water before consumption is a simple and effective method to reduce pesticide residue. Scrubbing the skin gently with a brush can further enhance the cleaning process.
Choosing organically grown green apples, which are cultivated without synthetic pesticides, is another strategy to minimize exposure. However, it’s important to note that even organic produce may contain some naturally occurring pesticides or residues from other sources. The choice between conventionally grown and organically grown apples often comes down to personal preference and budget considerations, alongside a balanced assessment of potential risks and benefits.
FAQ Compilation
Are green apples good for diabetics?
Green apples have a relatively low glycemic index compared to some other fruits, meaning they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels. However, portion control is still important for individuals with diabetes.
Can I eat the apple skin?
Yes! The skin contains a significant portion of the fiber and many beneficial nutrients. Thoroughly washing the apple before consumption is recommended, especially if it’s conventionally grown.
How long can I store green apples?
Properly stored in a cool, dry place, green apples can last for several weeks. Refrigeration can extend their shelf life even further.
Are there any known allergies to green apples?
While rare, apple allergies do exist. Symptoms can range from mild itching to severe reactions. If you experience any adverse reactions after consuming apples, consult a doctor.
What are the best ways to prepare green apples?
Green apples can be enjoyed raw, juiced, baked, or incorporated into salads, sauces, and desserts. The preparation method will influence the overall texture and flavor profile.
