Nutritional Composition of Two Eggs
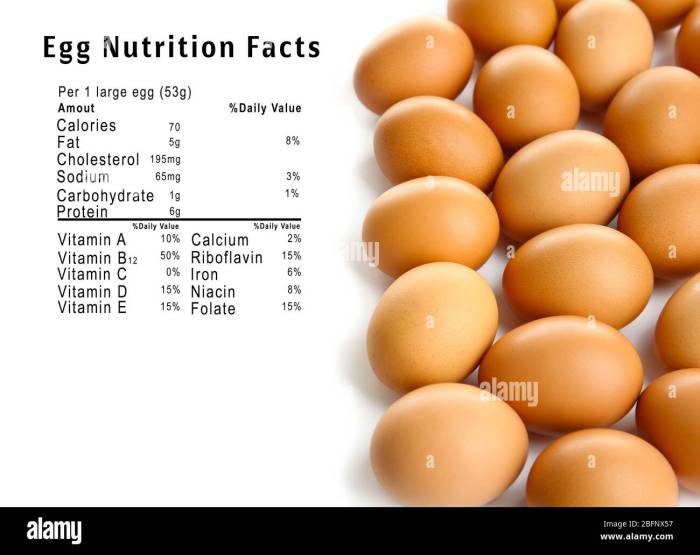
2 eggs nutrition facts – Two large eggs offer a surprisingly diverse and nutrient-rich profile, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Understanding their macronutrient and micronutrient composition allows for informed dietary choices and helps in achieving optimal nutritional intake. This section will detail the nutritional breakdown of two large eggs, comparing their contribution to the recommended daily intake for an average adult.
Macronutrient Composition of Two Eggs
The following table presents a detailed breakdown of the macronutrients – protein, fat, and carbohydrates – found in two large eggs (approximately 100g). Values may vary slightly depending on factors such as egg size and hen breed. Daily values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet.
| Nutrient | Amount per Two Eggs (approx.) | % Daily Value (approx.) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 155 | – | kcal |
| Protein | 12g | 24% | g |
| Fat | 10g | 15% | g |
| Saturated Fat | 3g | 15% | g |
| Carbohydrates | 1g | <1% | g |
Micronutrient Composition of Two Eggs
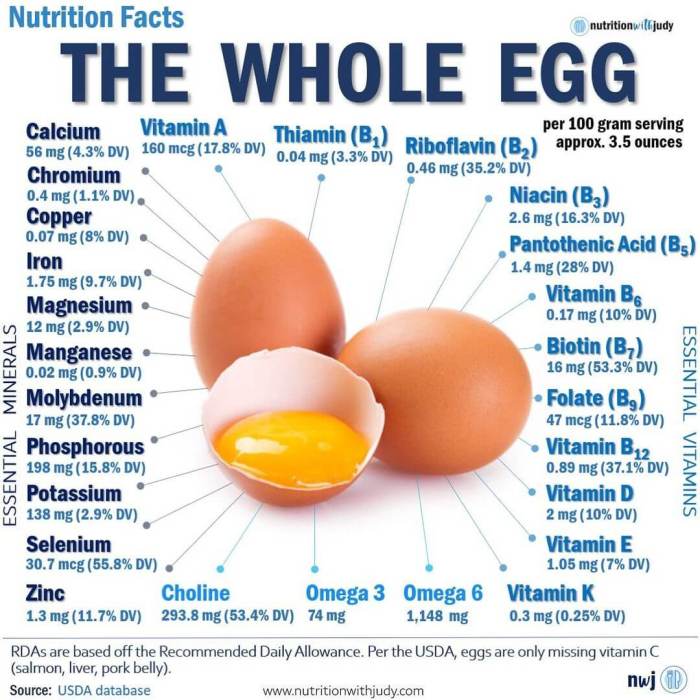
Two eggs are an excellent source of several essential vitamins and minerals, contributing significantly to daily nutritional needs.Eggs are a good source of:
- Vitamins: Vitamin A (supports vision and immune function), Vitamin D (essential for bone health and immune function), Vitamin E (an antioxidant), Vitamin K (important for blood clotting), several B vitamins (including B12, crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation, riboflavin, and biotin, involved in energy metabolism and cell growth).
- Minerals: Selenium (an antioxidant with roles in thyroid hormone metabolism), Choline (essential for brain development and liver function), Zinc (important for immune function and cell growth), Iron (vital for oxygen transport in the blood).
Comparison to Recommended Daily Intake
The nutritional profile of two eggs contributes a substantial portion of the recommended daily intake for several essential nutrients. For instance, the protein content in two eggs provides approximately 24% of the recommended daily intake for an average adult. Similarly, the egg’s vitamin and mineral content contributes significantly to daily needs. However, it’s crucial to remember that a balanced diet containing a variety of foods is essential to meet all nutritional requirements.
Two eggs alone do not constitute a complete diet. The percentage of daily value provided by two eggs varies depending on individual needs and overall caloric intake. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can help tailor dietary plans to meet individual nutritional requirements.
Health Benefits of Consuming Two Eggs
Consuming two eggs daily can offer a range of health benefits, stemming from their rich nutritional profile. While concerns about cholesterol have historically surrounded egg consumption, current research suggests that for most healthy individuals, the benefits often outweigh the risks. The following sections detail some key advantages associated with incorporating two eggs into a balanced diet.
Heart Health and Cholesterol, 2 eggs nutrition facts
The relationship between egg consumption and heart health is complex. While eggs are high in cholesterol, studies have shown that dietary cholesterol has a less significant impact on blood cholesterol levels than previously believed. The cholesterol found in eggs is primarily in the yolk, alongside healthy fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These healthy fats can contribute to improved HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels, which can help protect against heart disease.
Furthermore, eggs are a good source of choline, which plays a role in lipid metabolism and may help prevent the build-up of plaque in arteries. It’s important to note that individual responses to dietary cholesterol vary, and moderation remains key within a balanced dietary pattern.
Muscle Growth and Repair
Two eggs provide a significant amount of high-quality protein, essential for muscle growth and repair. They contain all nine essential amino acids, meaning your body cannot produce them and must obtain them through diet. These amino acids are the building blocks of muscle tissue, making eggs an excellent choice for individuals engaging in regular physical activity or looking to build and maintain muscle mass.
The protein in eggs is easily digestible and efficiently utilized by the body, contributing to optimal muscle protein synthesis. For example, a post-workout snack of two eggs can significantly aid muscle recovery and growth.
Two eggs offer a substantial protein boost and essential nutrients, providing a good start to the day. However, if you’re curious about the nutritional profile of a different kind of treat, you might want to check out the reese’s cup nutrition facts , which offer a very different macronutrient breakdown. Returning to our initial focus, remember that the nutritional value of eggs varies depending on preparation methods and the size of the eggs.
Eye Health
Eggs are a good source of lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoids that are crucial for eye health. These antioxidants are concentrated in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Lutein and zeaxanthin help protect the eyes from damage caused by harmful blue light and free radicals, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts.
Regular consumption of foods rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, such as eggs, can contribute to maintaining healthy vision throughout life.
Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Choline, a nutrient abundant in eggs, is vital for brain health and cognitive function. It is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter crucial for memory, learning, and muscle control. Adequate choline intake is associated with improved cognitive performance and a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline. The choline in two eggs can contribute to maintaining healthy brain function, supporting optimal cognitive processes, and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Potential Health Concerns and Considerations
While two eggs offer numerous nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential health concerns associated with their consumption, particularly for individuals with specific health conditions or dietary restrictions. Understanding these considerations allows for informed choices regarding egg inclusion in one’s diet.The primary concern revolves around cholesterol. Eggs are naturally high in cholesterol, and for some individuals, particularly those with pre-existing high cholesterol or heart disease, consuming two eggs daily might contribute to elevated blood cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular issues.
However, research on the impact of dietary cholesterol on blood cholesterol is complex and evolving. While some studies show a correlation, others suggest that saturated and trans fats play a more significant role in raising LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Therefore, individual responses vary considerably.
Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Health
The relationship between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol is nuanced. While eggs contain cholesterol, the impact on individual blood cholesterol levels depends on various factors, including genetics, overall diet, and existing health conditions. For people with hypercholesterolemia or a family history of heart disease, it’s advisable to consult a doctor or registered dietitian before significantly increasing egg consumption.
They can assess individual risk factors and recommend appropriate dietary adjustments. For healthy individuals with no pre-existing conditions, moderate egg consumption is generally considered safe.
Individual Dietary Needs and Health Conditions
Incorporating eggs into a diet requires consideration of individual health circumstances. For example, individuals with diabetes need to monitor their carbohydrate intake, as eggs contain some carbohydrates. Those with kidney disease might need to limit protein intake, and eggs are a good source of protein. People with allergies, discussed below, must completely avoid eggs. A balanced approach is key, considering both the nutritional benefits and potential risks in the context of one’s overall dietary plan and health status.
Egg Allergies
Egg allergies are a significant concern for a subset of the population. These allergies can range from mild to severe, with symptoms including hives, itching, swelling, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition. Egg allergies are often diagnosed through skin prick tests or blood tests conducted by allergists. Management involves strict avoidance of eggs and egg products, including hidden sources like mayonnaise or baked goods.
Individuals with known egg allergies should always carefully read food labels and inform restaurants and caterers about their allergy. In cases of severe allergy, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is essential.
Comparison of Different Egg Types
| Egg Type | Nutritional Profile (per egg) | Cholesterol (mg) | Potential Health Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Egg | Similar nutritional content to brown eggs, slightly lower in calories | ~185 | Similar health benefits and risks as brown eggs; cholesterol content remains relatively consistent. |
| Brown Egg | Generally similar nutritional content to white eggs, slight variations in certain nutrients | ~185 | Similar health benefits and risks as white eggs; cholesterol content remains relatively consistent. Variations in nutritional content are minor and unlikely to significantly impact health. |
| Free-Range Egg | Often higher in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E compared to caged eggs | ~185 | Potential additional health benefits due to higher omega-3 content; cholesterol content remains relatively consistent. |
FAQ: 2 Eggs Nutrition Facts
Are brown eggs more nutritious than white eggs?
The nutritional differences between brown and white eggs are minimal. The color difference is due to the breed of hen, not the nutritional content. Both offer similar amounts of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
How many eggs are too many to eat in a day?
For most healthy adults, consuming up to one or two eggs per day is generally considered safe. However, individuals with high cholesterol should consult their doctor about appropriate egg consumption.
Can I eat eggs if I have a cholesterol problem?
The impact of dietary cholesterol on blood cholesterol levels is less significant than previously thought. However, individuals with high cholesterol should consult their doctor or a registered dietitian to determine a suitable level of egg consumption.
What are some creative ways to incorporate eggs into my diet beyond breakfast?
Eggs are incredibly versatile! Consider adding them to frittatas for lunch, quiches for dinner, or using them as a binder in meatballs or meatloaf.
